Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Using adaptive regularization#
Adaptive or iteratively re-weighted regularization is a technique that can improve feature selection properties over the standard Lasso and Group Lasso extensions. In this example we compare the performance of the standard Lasso with adaptive Lasso.
Lasso performance metrics:
train r2: 0.969
test r2: 0.952
train rmse: 37.434
test rmse: 42.415
Adaptive Lasso performance metrics:
train r2: 0.970
test r2: 0.958
train rmse: 36.521
test rmse: 40.001
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import make_regression
from sklearn.linear_model import Lasso
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, r2_score
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV, KFold, train_test_split
from sparselm.model import AdaptiveLasso
X, y, coef = make_regression(
n_samples=200,
n_features=100,
n_informative=10,
noise=40.0,
bias=-15.0,
coef=True,
random_state=0,
)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.25, random_state=0
)
# create estimators
lasso = Lasso(fit_intercept=True)
alasso = AdaptiveLasso(max_iter=5, fit_intercept=True)
# create cv search objects for each estimator
cv5 = KFold(n_splits=5, shuffle=True, random_state=0)
params = {"alpha": np.logspace(-1, 1, 10)}
lasso_cv = GridSearchCV(lasso, params, cv=cv5, n_jobs=-1)
alasso_cv = GridSearchCV(alasso, params, cv=cv5, n_jobs=-1)
# fit models on training data
lasso_cv.fit(X_train, y_train)
alasso_cv.fit(X_train, y_train)
# calculate model performance on test and train data
lasso_train = {
"r2": r2_score(y_train, lasso_cv.predict(X_train)),
"rmse": np.sqrt(mean_squared_error(y_train, lasso_cv.predict(X_train))),
}
lasso_test = {
"r2": r2_score(y_test, lasso_cv.predict(X_test)),
"rmse": np.sqrt(mean_squared_error(y_test, lasso_cv.predict(X_test))),
}
alasso_train = {
"r2": r2_score(y_train, alasso_cv.predict(X_train)),
"rmse": np.sqrt(mean_squared_error(y_train, alasso_cv.predict(X_train))),
}
alasso_test = {
"r2": r2_score(y_test, alasso_cv.predict(X_test)),
"rmse": np.sqrt(mean_squared_error(y_test, alasso_cv.predict(X_test))),
}
print("Lasso performance metrics:")
print(f" train r2: {lasso_train['r2']:.3f}")
print(f" test r2: {lasso_test['r2']:.3f}")
print(f" train rmse: {lasso_train['rmse']:.3f}")
print(f" test rmse: {lasso_test['rmse']:.3f}")
print("Adaptive Lasso performance metrics:")
print(f" train r2: {alasso_train['r2']:.3f}")
print(f" test r2: {alasso_test['r2']:.3f}")
print(f" train rmse: {alasso_train['rmse']:.3f}")
print(f" test rmse: {alasso_test['rmse']:.3f}")
# plot model coefficients
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
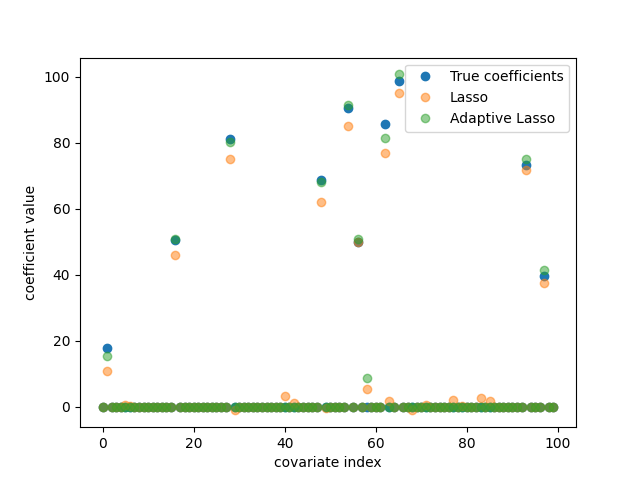
ax.plot(coef, "o", label="True coefficients")
ax.plot(lasso_cv.best_estimator_.coef_, "o", label="Lasso", alpha=0.5)
ax.plot(alasso_cv.best_estimator_.coef_, "o", label="Adaptive Lasso", alpha=0.5)
ax.set_xlabel("covariate index")
ax.set_ylabel("coefficient value")
ax.legend()
fig.show()
# plot predicted values
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
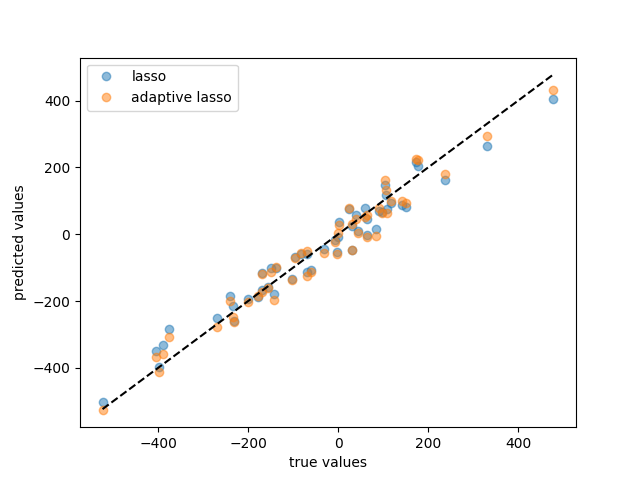
ax.plot(y_test, lasso_cv.predict(X_test), "o", label="lasso", alpha=0.5)
ax.plot(y_test, alasso_cv.predict(X_test), "o", label="adaptive lasso", alpha=0.5)
ax.plot([y_test.min(), y_test.max()], [y_test.min(), y_test.max()], "k--")
ax.set_xlabel("true values")
ax.set_ylabel("predicted values")
ax.legend()
fig.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 3.129 seconds)